Advantage AxisDirect
- 20 investment products
- 3 great platforms to invest
- 5 fun-tastic learn courses
- 5 powerful research segments
- 4 prestigious awards
- 9 lakh+ happy investors
Quotes
Back To Menu
-
Offerings
- Overview
- Products
- DIGITAX
- Managed Accounts
- Private Client Group
- Business Associates
- NRI
- Refer & Earn
- Insurance
- SGB
- Investment Advisory
- Markets
- Research
- Learn
- PORTFOLIO
- PROFILE
Series 28: Stochastic Oscillator
Jan 28, 2025

Series 28: Stochastic Oscillator
The Stochastic Oscillator is a popular momentum indicator used in technical analysis to compare a stock's closing price to its price range over a specified period. Developed by George Lane, the Stochastic Oscillator is a bounded indicator that oscillates between 0 and 100, helping traders identify overbought or oversold conditions in the market. It is widely used to assess the strength of a trend, potential reversal points, and momentum shifts.
The key idea behind the Stochastic Oscillator is that prices tend to close near their highs in an uptrend and near their lows in a downtrend. A reading above 80 indicates that the stock is in the overbought zone, while a reading below 20 indicates that the stock is in the oversold zone. However, these levels are not absolute and should be used in conjunction with other technical indicators and trend analysis for confirmation.
How is the Stochastic Oscillator Calculated?
The Stochastic Oscillator is calculated using the following formula:
%K = ((Current Close - Lowest Low) / (Highest High - Lowest Low)) * 100
Where:
Current Close = The most recent closing price.
Lowest Low = The lowest price over the specified period (typically 14 days).
Highest High = The highest price over the specified period (typically 14 days).
Additionally, a smoothed moving average of %K, called %D, is often used as a signal line:
%D = 3-day Simple Moving Average of %K
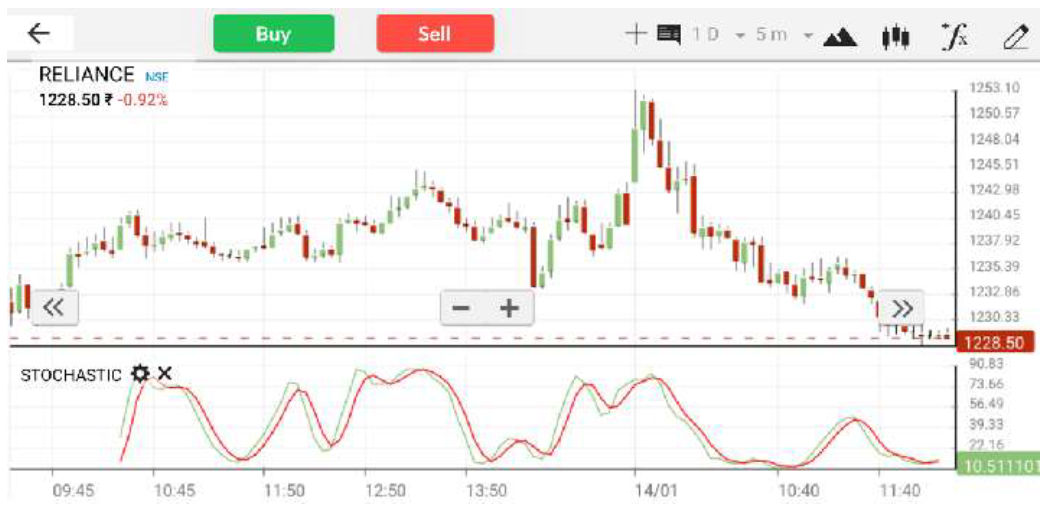
Example: Reliance Industries
Let’s assume the closing prices of Reliance Industries for the past 7 days were as follows:
Day 1: ₹1200
Day 2: ₹1210
Day 3: ₹1225
Day 4: ₹1230
Day 5: ₹1215
Day 6: ₹1220
Day 7: ₹1235
Step 1 : Identify the Highest High and Lowest Low
Highest High = ₹1235 (Day 7)
Lowest Low = ₹1200 (Day 1)
Step 2: Calculate %K for Day 7
Using the formula :
%K = [(Current Close - Lowest Low) / (Highest High - Lowest Low)] × 100
For Day 7:
Current Close = ₹1235
Lowest Low = ₹1200
Highest High = ₹1235
%K = [(1235 - 1200) / (1235 - 1200)] × 100
%K = [35 / 35] × 100 = 100
Step 3: Calculate %D
To calculate %D, take the 3-day simple moving average of %K. For simplicity, assume the %K values for the last 3 days are:
Day 5: 60
Day 6: 80
Day 7: 100
%D = (60 + 80 + 100) / 3 = 80
Thus, for Day 7:
%K = 100
%D = 80
How to Interpret the Stochastic Oscillator?
1. Overbought and Oversold Levels:
- ● %K > 80: The stock is considered overbought, which may indicate a potential reversal or pullback.
- ● %K < 20: The stock is considered oversold, which may indicate a potential reversal or upward movement.
- ● The Stochastic Oscillator can remain overbought or oversold for a prolonged period in a trending market.
2. Crossovers:
- ● A bullish crossover occurs when %K crosses above %D in the oversold zone.
- ● A bearish crossover occurs when %K crosses below %D in the overbought zone.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only. Consult a financial advisor before engaging in such trading activities.
Axis Direct Disclaimer This is for educational purposes only. Axis Direct is a brand under which Axis Securities Limited offers its. Retail broking and investment services. Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks. Read all the related documents carefully before investing. Disclaimer & Statutory Information
Related Keyword
Technicals
Options
Call Centre
Put Option
Futures
TechnicalAnalysis
Similar Articles
Show more...




 India
India NRI
NRI